
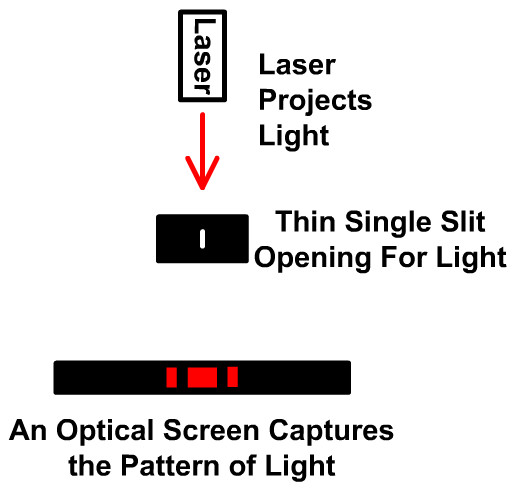
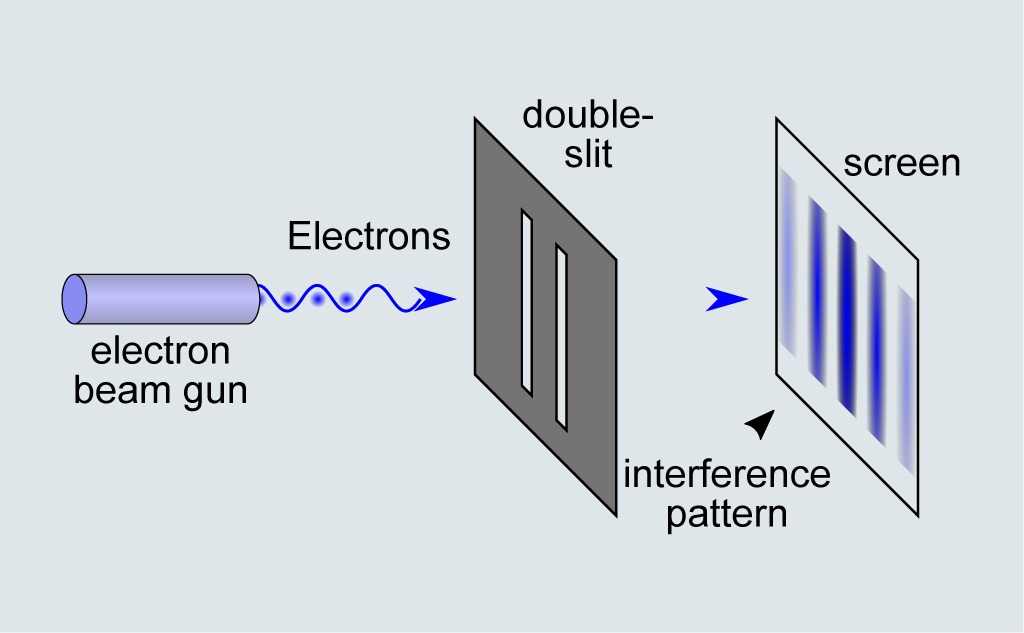
On the other hand, in electron-scattering experiments on crystalline structures, the electron behaves as a wave.Ī skeptic may raise a question that perhaps an electron might always be nothing more than a particle, and that the diffraction images obtained in electron-scattering experiments might be explained within some macroscopic model of a crystal and a macroscopic model of electrons coming at it like a rain of ping-pong balls. Likewise, in the Compton scattering of X-rays on electrons, the electron is a particle. In Bohr’s early quantum theory of the hydrogen atom, both the electron and the proton are particles of matter. This discovery changed the way in which electricity is understood today and gave the electron its particle status. Thomson’s experiment showed that the unit of negative electric charge (an electron) can travel in a vacuum without any medium to carry the charge around, as in electric circuits. Within this theory of electric fluid, the present theory of electric circuits was developed, and electromagnetism and electromagnetic induction were discovered. Thomson’s discovery of the electron in 1897, electric current was seen as a flow in a continuous electric medium. From Benjamin Franklin’s observations of electricity in 1751 until J.J. For light, this mechanism creates a bright-and-dark fringe pattern on the viewing screen.Ī similar dichotomy existed in the interpretation of electricity. At positions marked “Min,” the combined wave amplitude is zero. At the positions marked “Max” on the screen, the meeting waves are in-phase and the combined wave amplitude is enhanced. They travel from their origins at the slits to the viewing screen placed to the right of the slits. Two waves are generated at the positions of two slits in an opaque screen. Maxwell’s classical view of radiation as an electromagnetic wave is still valid today however, it is unable to explain blackbody radiation and the photoelectric effect, where light acts as a beam of photons.įigure 6.23 Young’s double-slit experiment explains the interference of light by making an analogy with the interference of water waves. In James Clerk Maxwell’s theory of electromagnetism (completed by the year 1873), light is an electromagnetic wave. The corpuscular hypothesis failed in 1803, when Thomas Young announced his double-slit interference experiment with light (see Figure 6.23), which firmly established light as a wave. According to Newton, a beam of light is a collection of corpuscles of light. It was already present in a debate between Isaac Newton and Christiaan Huygens about the nature of light, beginning in the year 1670. This dualistic interpretation is not a new physics concept brought about by specific discoveries in the twentieth century. Conversely, under some physical circumstances electromagnetic radiation acts as a wave, and under other physical circumstances, radiation acts as a beam of photons. All we can say is that wave-particle duality exists in nature: Under some experimental conditions, a particle appears to act as a particle, and under different experimental conditions, a particle appears to act a wave. At our present state of knowledge, such questions about the true nature of things do not have conclusive answers.

Is an electron a wave or is it a particle? The same question can be extended to all particles of matter-elementary particles, as well as compound molecules-asking about their true physical nature. The same electron behaves as a wave when it passes through a solid crystalline structure and forms a diffraction image. For example, an electron that forms part of an electric current in a circuit behaves like a particle moving in unison with other electrons inside the conductor. Therefore, the question arises about the nature of electromagnetic radiation: Is a photon a wave or is it a particle? Similar questions may be asked about other known forms of energy. The same energy of radiation detected by a photocurrent in the photoelectric effect comes as the energy of individual photon particles. The energy of radiation detected by a radio-signal receiving antenna comes as the energy of an electromagnetic wave. Summarize the evolution of scientific thought that led to the development of quantum mechanics.
Describe the physics principles behind electron microscopy.Identify phenomena in which electromagnetic waves behave like a beam of photons and particles behave like waves.By the end of this section, you will be able to:


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
